Date: 09-10-24
Problem
- In this problem we are given a BST and an empty array. Our code should create three functions that each do
in-order,pre-order, andpost-ordertree-traversal on the given BST and add the values to the empty array. - In-order:
- As the name suggests
in-ordertraverses the tree in order of the values. Starting from the root node we want to traverse to the leftmost node inorderTraverse(left) -> array.append(current val) -> inorderTraverse(right)
- As the name suggests
- Pre-order
- Visits the root node first, then traverses the left subtree and simultaneous adds it to the array, and the follows with the right subtree
- Post-order
- Visits the left subtree first, then the right subtree, and the root node is visited last.
Example:
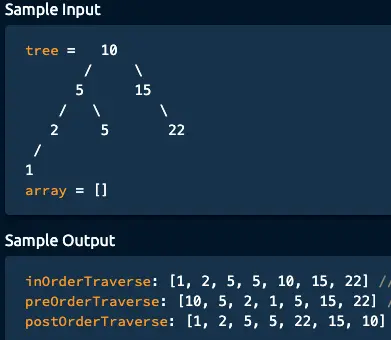
Approach 1:
- In this approach we are using recursion to traverse the BST. Similar to all traversals we are first going left and depending on the traversal method we append the value before a certain point or in the middle, or at the end of the BST. We are also initially checking if tree is not None, if it is then we simply return the empty array.=
Implementation
def inOrderTraverse(tree, array):
# if tree is not empty
if tree is not None:
inOrderTraverse(tree.left, array)
# -> inOrderTraverse(tree.left.left, )
array.append(tree.value)
inOrderTraverse(tree.right, array)
return array
def preOrderTraverse(tree, array):
if tree is not None:
array.append(tree.value)
preOrderTraverse(tree.left, array)
preOrderTraverse(tree.right, array)
return array
def postOrderTraverse(tree, array):
if tree is not None:
postOrderTraverse(tree.left, array)
postOrderTraverse(tree.right, array)
array.append(tree.value)
return arrayComplexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: — O(N) due to the creation of the array, but without the array it would be O(d) or the depth of the BST due to call stack from the recursion