Date: 08-03-24
Understanding the Problem

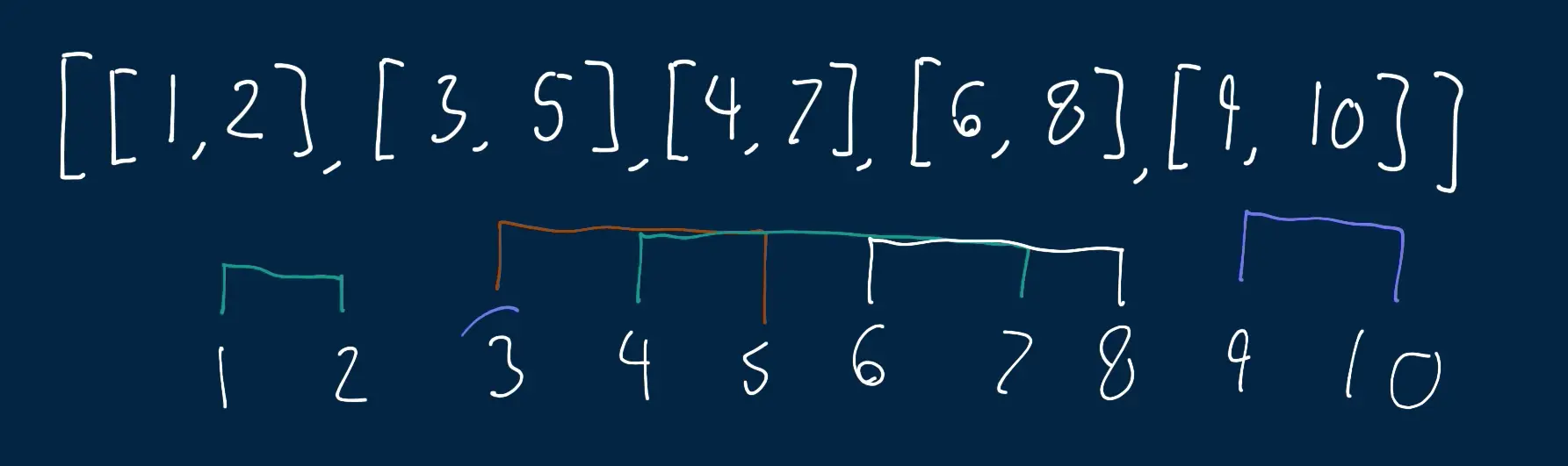
- In this problem the input is a non-empty array of arbitrary intervals. Our solution is required to merge any overlapping intervals, for instance, if theres an interval
[3, 5], [4, 7], we know that 4 overlaps in both intervals therefore our solution should merge these into[3,7]. Finally, we return the new intervals (2d array) once we’re doing merging all overlapping intervals (the order of these intervals is not important).
Example
intervals = [[1, 2], [3, 5], [4, 7], [6, 8], [9, 10]]
Output:
[[1, 2], [3, 8], [9, 10]]Approach 1
- In this solution the way we can check for overlapping intervals is to check the end value of interval compare to the start value of the second interval. If the end of the first interval is greater than or equal to start of the second interval then we know we have overlapping intervals and need to merge them. This works when interval one is sorted relative to interval two, however, if we do the same comparison and they’re switched we end up triggering a false overlap. This is because, for instance
1: [3, 4] 2: [1, 2], if we compare the end to the start, we see that4 >= 1but these two intervals are not overlapping - To solve for this comparison issues, we need to first sort the intervals based on the starting value.
Algorithm
- Define an output array to store the new merged intervals
- Sort the input array based on the first element of the intervals
- Begin iterating over the input array comparing the first element of the current interval with the previous interval and its second element. In the instance of the first element in the input array there’s nothing to compare it, therefore we just place it in the output array
- We keep iterating until we’ve reached a comparison that overlaps
- If we find a merging interval we just need to modify the last interval in the output array and its ending element. To find which value belongs in the ending element of that interval we simply find the
maxof the ending of both overlapping intervals.
Implementation
# O(n log(n)) time | O(n) space
def mergeOverlappingIntervals(intervals):
# Sort intervals based on the first value of the intervals
sortedIntervals = sorted(intervals, key=lambda x: x[0])
# Output array
mergedIntervals = []
# Since our algorithm requires comparing to our output array and the first interval has nothing to compare
# to we can simply add it to the output array. This is also assume we're given at least on element in the input array
currentInterval = sortedIntervals[0]
mergedIntervals.append(currentInterval)
# NOTE: since we assign current interval to the first value of sortedIntervals and then append it
# to the mergedIntervals array, now we have an array within an array therefore the any changes made
# to currentInterval will also modify mergedIntervals which is the output array
# Iterate through input array
for nextInterval in sortedIntervals:
# _ we're using this notation because we don't care about the first element and just the second element
# This decomposes the interval in to _ and currentIntervalEnd
_, currentIntervalEnd = currentInterval
# Next, we define nextIntervalStart and nextIntervalEnd
nextIntervalStart, nextIntervalEnd = nextInterval
# if the end of the previous interval is greater than or equal to the start of the current interval in the input array
# e.g. ([1, 3], [2, 4]) - > [1, 4]
# then we can begin to merge
if currentIntervalEnd >= nextIntervalStart:
# since they overlap we check interval between the two has the greter ending.
# this way they don't overlap again and we can mutate the end to be the max
# currentInterval will modify the mergedIntervals array too
currentInterval[1] = max(currentIntervalEnd, nextIntervalEnd)
else:
# if case is not true set the current interval to the current index in the array
# and append it to the final output array
currentInterval = nextInterval
mergedIntervals.append(currentInterval)
return mergedIntervalsComplexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: