Date: 08-03-24
Problem
- We are given an array of integers between 1 and n, inclusive where
nis the length of the array. We need to write a function that returns the first integer that appears more than once (when read from left to right). If no integer appears more than once, our function should return-1. - Note: You’re allowed to mutate the input array
Example
- In this example we see that two repeats first, therefore we return the value that repeats first.
Solution
- Two for loops (brute force):
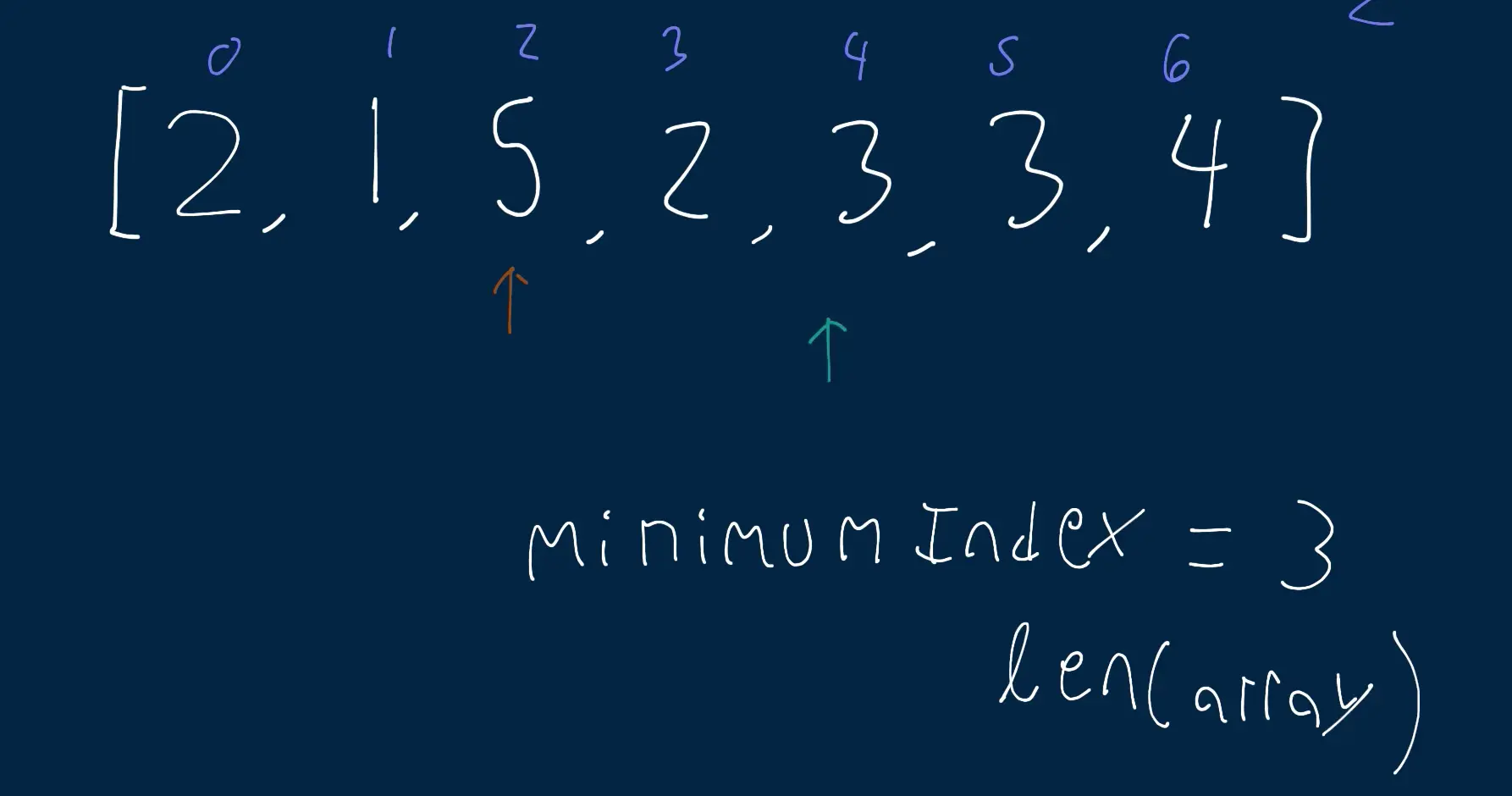
- in this solution we are using two for loops and a minimum index. Our outer loop keeps track of the current index and the inner loop tries to find the duplicate value
- The minimum index is initially set to the length of the array which makes sense, since there could be instance where theres no minimum index found and we just return
-1. However, if we do find a new minimum index then we useminfunction to find the minimum of the current value of minimum index and the new one. - we continue this until we’ve iterated over the entire array.
- Time complexity : | Space complexity:
- Set solution
- This solution is much more simple and runs in linear time.
- For this solution we create a set called
seen, where we add the numbers one by one in the array. if the number is not in the set we add it, however, if we see that a number is already in the set than we know we can return this value. Since this will be the first repeated value and theres no need to keep traversing.

- Time complexity: | Space complexity:
- It’s important to note that checking a set is an O(1) operation, however if we had a different data structure than we would need to multiply the time complexity of this operation to the iteration of the array
- Optimal Solution
- To get to this most optimal solution it’s important to note the information we were given. For instance we’re told that the range of this array is between 1 and n, where n is the length of the array. Alongside this, we’re told that we are allowed to mutate this input array.
- Taking advantage of these details we can deduct the following
- since our array is in the range of
1...n. we can sort of create a map within the array to be able to detect if we’ve found a duplicate value. - The way this mapping will working is that we will use the indices and their values to map between values already checked.

- For instance, in our first index our first mapping index will be
2 - 1 = index, where index will equal 1. This means that the value 2 appearing will be represented by the index 1. And for the second index we will do1 - 1 = 0therefore the index at 0 will represent value 1. - However, this alone is not useful for us we need a way to indicate that this new index was mapped, so if we ever run into again then we know we have a repeating value.
- Lets run through an iteration example
- First, we check what the index maps the value 2, in this case it would be
2- 1 = 1. Then we look at index one in the array and we’re going to see what value is there. And we’re going to check if this value is negative. If it is not negative then we’re going to set this value to negative. This is going to be our way of indicating that we’ve mapped this index before. - Great, now we keep moving on through the array. For our second index our new value will be -1. To not mess up our way of mapping our new indices we can wrap our formula in an absolute value so this
value - 1 = indexwill now beabs(value) - 1 = index. This prevents our mapping from getting messed up and we continue. Therefore for the second iteration we’ll haveabs(-1) - 1 = index. index = 0. Then we check the value at index 0, if it’s negative than that means we’ve mapped to this index before if it is not then we set the value to negative and move on the next index in the array. - Great now for 5 we will have
abs(5) - 1 = 4. we check the value at index 4 and we see that its not negative so wasn’t already mapped through. therefore, we set the value to negative and move on the next index in the array. - Next we reach the value 3, we do the calculation
abs(3) - 1 = 2. we check the value at index 2 and we see that is negative therefore we’ve mapped through this index before and the way this is only possible is that if we have the samevaluein this mapping formulavalue - 1 = index. Therefore we return the value 3 and we’ve solved the problem. - This solution runs in time and space. We’re doing one iteration through the array and we’re using the same input array therefore constant space.
- First, we check what the index maps the value 2, in this case it would be
- since our array is in the range of