Date: 08-05-24
Problem
- We’re given an input array and we need to find the zero sum subarray (numbers that add up to 0). The min length of this subarray can be 1 and the maximum can be the length of the array. We return
TrueorFalse.
Example:
nums = [4, -3, 2, 4, -1, -5, 7] -> [2, 4, -1, 5] = 0, Therfore TrueApproach 1:
- To find if there’s a zero sum in this array we will use the fact that if we find the sum as we iterate through the array if there’s two duplicate values then we know that these values if subtracted or separated (sub array) will equal to 0.
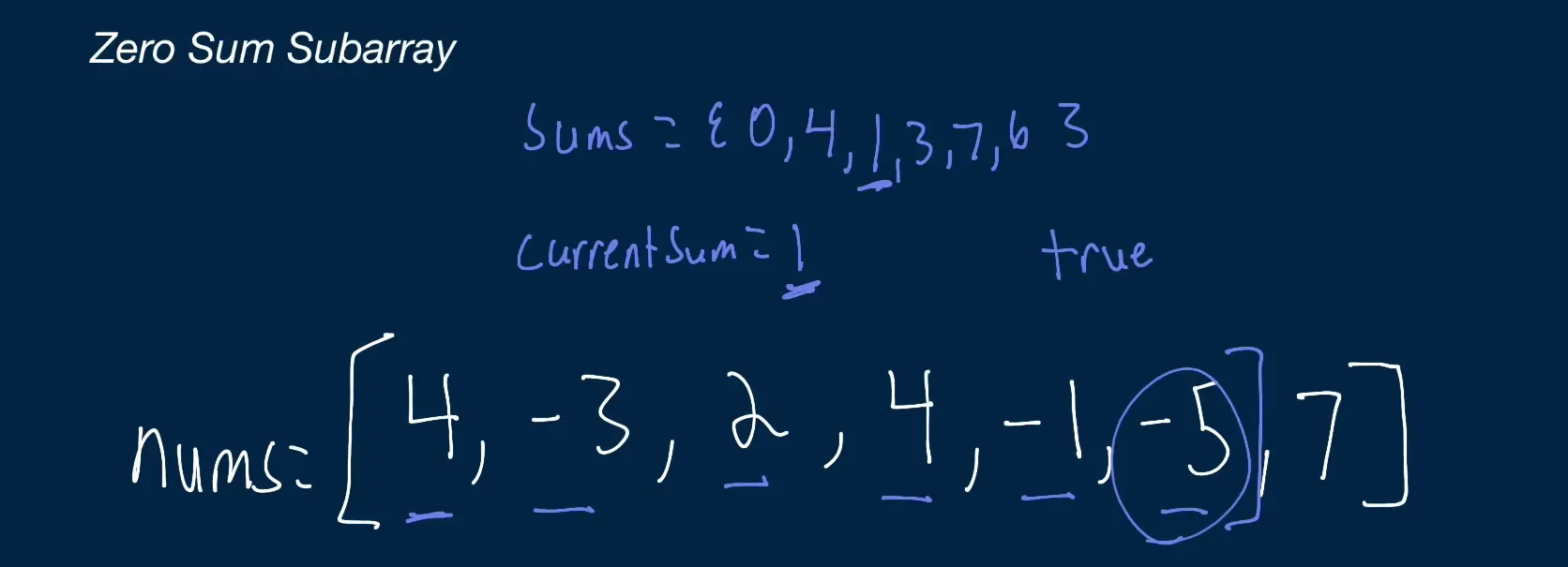
- For instance in this example we calculated one at the subarray [4, -3] then as we moved on with the running sum we also calculated 1 at the index of
-5. Meaning our zero sum subarray will begin at the index of the first duplicate value plus one. This is essentially separating the subarray or subtracting from it to equate it to 0. Therefore in this instance our subarray would be[2, 4, -1, -5]. - To accomplish this we use the set called
sumswhich will be initialized with a zero since we will refer to index of this set to find first duplicate value. Then we use currentSum which as the name states will keep track of the current running sum and add the value to the sums set. For each time we add a new value to the set we check if this value exists already if so then return True else continue until we’ve reached the end of the array and return False.
Implementation
def zeroSumSubarray(nums):
# Sums set and current sum
sums = set([0])
currentSum = 0
# Begin iteration
for num in nums:
# Calculate current sum
currentSum += num
# if the current sum is in nums then we know we have zero sum subarray
if currentSum in sums:
return True
# otherwise add the current sum to sums set
sums.add(currentSum)
return FalseComplexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: — Sums can be of n space in the worst case scenario.